What are binaural beats?
The science behind binaural beats is not very complicated: When you hear two tones — one in each ear — that are slightly different in frequency, your brain processes a beat at the difference of the frequencies. This is called a binaural beat.
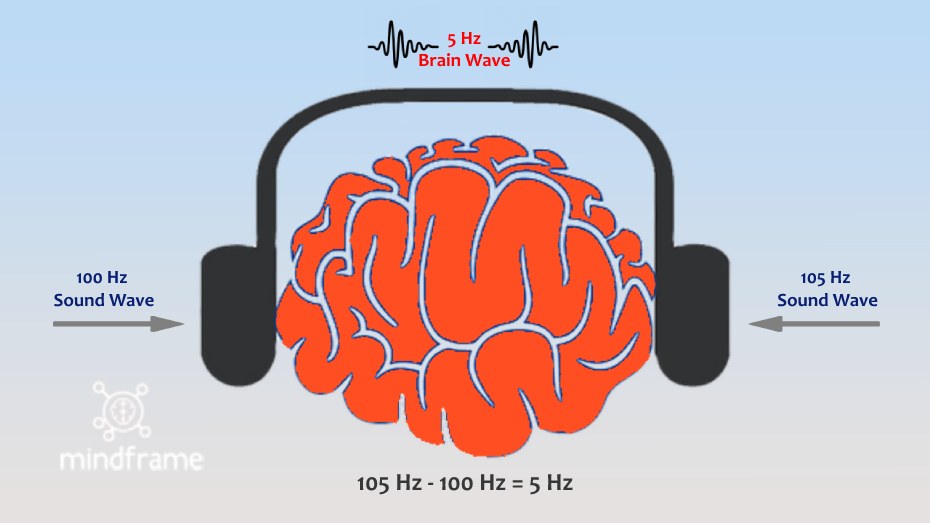
For example:
If a 100 Hz sound frequency is sent to the left ear, and a 105 Hz to the right ear, your brain gradually falls into synchrony with the difference at 5 Hz (which is in the Theta range). Instead of hearing two different tones, you instead hear a tone at 5Hz (in addition to the two tones given to each ear).
Binaural beats are therefore a type of “brainwave entrainment”, a process in which the natural wavelengths of the brain are trained or synchronized to fall into a specific type of brainwave that corresponds with a desired mental state (e.g. sleep, awareness, etc.).
Brainwave Frequencies: What are they?
Brain waves represent patterns of electrical activity produced by the brain. The brain is made up of billions of neurons that use electrical signals to transmit information.
When groups of neurons fire together in a certain way to send signals to other groups of neurons, the resulting patterns are known as brain waves. These electrical patterns are associated with different types of activity in the brain as well as different states of consciousness.
There are 5 major types of brain waves:
- Delta waves: (frequency of 1 – 4 Hz) are associated with deep states of dreamless sleep. In several studies, people who received a delta pattern frequency during sleep entered a deeper stage of sleep, according to electroencephalogram (EEG) brain scan results.
- Theta waves: (frequency of 4 – 7 Hz) are associated with REM sleep, deep relaxation, meditation and creativity.
- Alpha waves: (frequency of 7 – 13 Hz) are associated with relaxed focus, stress reduction, positive thinking and learning – a good beat to accompany meditation. May encourage relaxation.
- Beta waves: (frequency of 13 –30 Hz) are associated with focused attention, cognitive thinking and problem solving – also good to listen to while working from home! These are the waves that occur during most conscious, waking states. However, it can also increase anxiety at the higher end of the range.
- Gamma waves: (frequency of 30–50 Hz) are associated with peak awareness, memory recall, learning, problem-solving, and information processing.
How do you use binaural beats?
All you need to experiment with binaural beats is a binaural beat audio and a pair of headphones or earbuds (you must use for binaural beats to work).
You can easily find audio files of binaural beats online, such as on YouTube or via downloaded audio files to your mp3 player or mobile device.
Here is an example of a Theta Binaural Beat at 4 Hz (which is good for meditation):
Here is one for focus and concentration at 13hz (Beta)
Lastly, you’ll want to do a search and try out several to find the ones that work for you. Everybody reacts differently.
Remember, you must use headphones for binaural beats to work. You may also want to listen with your eyes closed.
The bottom line
With several human studies to back up the health claims, binaural beats appear to be a potential tool in the fight against anxiety, stress, and negative mental states.
moreover, research has found that listening daily to audio with binaural beats may have potential benefits which include:
- reduced stress and anxiety
- increased focus, concentration, and motivation
- improved confidence
- better long term memory after exposure to beta pattern frequencies, according to a 2019 study
- enhanced mood
- deeper meditation
Binaural beats won’t work for everyone, and they aren’t considered a cure for any particular condition.
However, they might offer an auditory escape for those interested in relaxing, sleeping more peacefully, or entering a meditative state.